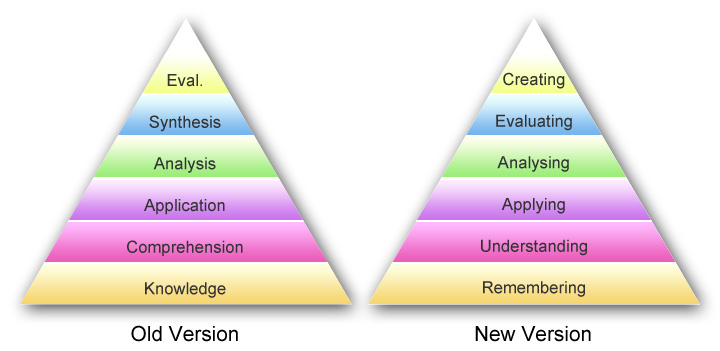
The tool to help creating action-based learning objectives is Bloom’s Taxonomy of thinking skills. Bloom’s Taxonomy is a tier model of classifying thinking according to 6 cognitive domains. Each level has action verbs associated with the domain. The Taxonomy has been used as a guideline for creating objectives which show evidence of thinking skills beginning at the Lower Order Thinking Skills to the Higher Order Thinking Skills since 1950s.
A little bit of history:
In the 1990s the original Taxonomy was revised by a student of Bloom’s who made three significant changes:
- changing the names in the six categories from noun to verb forms
- rearranging them as shown in the chart below
- creating a processes and levels of knowledge matrix
The Taxonomy builds from the Lower Order Thinking Skills to the Higher Order Thinking Skills and traditionally has been represented as a pyramid, showing how skills as building blocks. However more and more often the Taxonomy is being represented in a circular form to emphasize the importance and interconnectedness of every level of thinking skills. It is also a more fluid representation of the stages,:
Let’s take a look at the full set of objectives:
- After watching “Everything is a Remix” series (condition) students will be able to distinguish (performance) between original material and remixed material on the internet by creating an outline of their own remix of a popular movie trailer (criteria).
- After reading an article and the interview with Lawrence Lessig (condition) students will be able to recognize (performance) issues with copyright violations as a key element when borrowing someone else’s work on the Internet. — NEED CRITERIA
- After watching “Embracing the Remix” TedTalk from Kirby Furguson (condition) students will be able to discuss (performance) how the recycling of old culture makes a new one using the key points outlined in the talk (criteria).
The verbs used in the objectives represent different cognitive domains in the Taxonomy:
- distinguish – Comprehension
- recognize – Knowledge
- discuss – Evaluation
In writing these objectives we targeted three levels of thinking skills from lower level I – Knowledge, to level II – Comprehension, and finally, level VI – Evaluation thus targeting critical thinking skills in both higher and lower order.
_________________________________________________
Activity 1:
Using RadioJames Objective Builder – http://teachonline.asu.edu/objectives-builder/, choose one topic in your course. Create at least three learning objectives defining what students will need to do in order to demonstrate the evidence of acquired knowledge. Each objective should include Performance, Condition, and Criteria elements and an indication of Bloom’s Taxonomy level. Post your objectives in Comments section on this page.
_________________________________________________
Activity 2:
Check your Knowledge: distinguish between good and bad objectives
Based on what you have learned at this workshop, from the examples below, select TRUE if it is an example of a well-written objective; FALSE if it is not a well-written objective.
References:
Clark, D. (n.d.). Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Domains. Retrieved October 7, 2015, from http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/bloom.html
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy. (n.d.). Retrieved October 8, 2015, from http://teaching.uncc.edu/learning-resources/articles-books/best-practice/goals-objectives/writing-objectives